How do ASPUR air purifiers work
Published by ASPUR air solutions in Technology · Wednesday 26 Jan 2022
Tags: ASPUR air purifiers features, Filtration steps in air purifiers
Tags: ASPUR air purifiers features, Filtration steps in air purifiers
How do ASPUR air purifiers work?
All ASPUR AIR air purifier models meet the technical requirements for infection control ventilation in medical areas.
Filters tested according to the EN 1822 standard are used to reliably filter out viruses, bacteria, pollen, spores, germs and other particles that are hazardous to health. Up to 99.995% of all particles are safely separated via the 5 filtration levels and a high-quality high-efficiency particulate air filter (HEPA, level H14). A carbon filter (activated carbon) also adsorbs odor particles. The built-in motor technology and its efficiency corresponds to the most powerful IE4/IE5 industry standard Super Premium Efficiency Technology (EC Motor Technology).
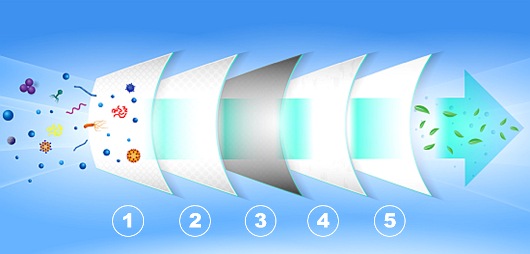
Filteration levels (structure):
(1) Pre-filter fleece G4
(2) Pre-filter G9 fiberglass fleece
(3) HEPA H14-filter
(4) Carbon filter (activated carbon)
(5) Post-filter fleece
Mechanisms of action of particle separation
The particle separation takes place via deep-bed filters, which on the one hand influence the transport of the particles to the filter and on the other hand the deposit of the particles through various separation mechanisms. It is filtered as the air flows past the fiber or filter mesh.
Particles are separated by four different, complementary mechanisms that work depending on the particle size:
1. Sieve effect: As the name suggests, the filter works like a sieve: Particles whose diameter is larger than the distance between the individual fibers get stuck in the filter.
2. Barrier effect: Small, light particles follow the air flow. Although the movement of the particle's center of mass leads past the filter fiber, it is so close to the individual fibers that they stick due to adhesive forces.
3. Inertial effect: Larger particles have a higher mass and therefore higher inertia and follow the air flow with a certain inertia. When the airflow changes direction because it goes around a fiber, the particle's inertia causes it to maintain its direction, bouncing against the fiber and sticking there.
4. Diffusion effect: Very small particles below 1 micrometer (μm) do not follow the flow lines around the filter fiber. They collide with other molecules on their way to the airflow (Brownian motion) and then change direction, also colliding with individual glass fibers where they then stick. The size of the particles has a decisive influence on the effect of the individual separation mechanisms. Due to the diffusion effect, very small, fine particles in particular are separated, while the blocking and inertia effect mainly dominates with particles with a diameter greater than 0.5 µm. With the sieve effect, it is the large particles that are filtered.

